JapanKnowledge
Explanatory Notes
"These introductory notes are taken from the paper edition."
I Introduction
1 This book traces with statistics the progress of Japan since the beginning of the Meiji era when the country took the first step toward modernization nearly one hundred and twenty years ago. It may serve as a historical series of the Japan Statistical Yearbook published since 1882 by the Statistics Bureau.
2 Since 1981, the Statistics Bureau, Management and Coordination Agency has compiled statistical data beginning the Meiji era through the present time on all fields including the land, population, economy, society and culture of Japan in order to provide historical statistics, principal items of which are contained herein. All of those data put in order, both included and not included herein, will be kept as the database of the historical statistics made available to general users.
3 Composition of the book
This book is composed of five volumes. Contents of each volume are as follows :
Preface
Foreword
Explanatory notes
General contents (all volumes)
List of tables (each volume)
Explanation, statistical tables, and note and source, by field
Besides those, volume 1 includes general remarks, "Statistical System in Japan," and volume 5 includes an index for all volumes.
Foreword
Explanatory notes
General contents (all volumes)
List of tables (each volume)
Explanation, statistical tables, and note and source, by field
4 Explanation by fields
At the beginning of each section, the system and history of each survey, revisions made of the survey, coverage and items to be surveyed, and the definition of terminology are explained in detail.
II Basic policy for compilation and editing
Data are compiled under the following basic policies.
1 In principle, sources of data are limited to those published by the government, government agencies and government-affiliated institutions.
2 In principle, original data are compiled over as long a historical period as possible, and only indispensable processing, such as conversion of units and computation for linking indexes, are made.
3 Data which are less important today but were important in a certain age are included as many as possible.
4 The primary data published by the agency engaged in the survey are used as original source ; however, in case the primary data, such as for the Meiji era, are not available, the secondary data, such as statistical yearbooks, are also adopted.
5 In case revised figures or final figures of a certain item were published later on, they are adopted wherever possible.
6 Data by year (calendar year, fiscal year, annual average, as of month, 19XX) are presented principally ; however , monthly data are also presented where they are especially significant.
7 In case different sources show different figures with no note or explanation accompanied on the same subject, a decision is made after judging the relationship with other items and the time-series of the statistics.
III Figures presented
1 For Okinawa
Beginning 1945, as statistical surveys have been conducted within the territory under the Japanese jurisdiction of the survey year, data on Okinawa are excluded from 1945 through 1972 unless otherwise noted. In various statistics by prefectures, Okinawa is indicated with "--."
However, as for the data on the population census, those by the Government of the Ryukyu Islands are available so that they are presented in the sections of population and labour.
However, as for the data on the population census, those by the Government of the Ryukyu Islands are available so that they are presented in the sections of population and labour.
2 Unit
Units of figures follow the original text.
3 Conversion of unit
The change in the measuring method from the shaku - kan system to the metric system adopted during this historical series brought considerable difficulty in comparing long-term data. Therefore, wherever applicable, units are converted to those of today. Footnotes indicate where the conversion was made and that it was made by the Statistics Bureau.
4 Calculation for linking indexes
The base year of various indexes has been renewed almost every five years. As periods retroacted are different according to each institution, it is not possible to find interrelation between them. Therefore, by adopting two bases, one on the average of 1934 through 1936 or the nearest period and the other on 1980, computation was made to link various indexes of different base. The linkage and the method of computation are indicated at the respective places.
5 Relationship between total and sum of items
Where figures are rounded or omitted because of unknown, they may not add up to the total.
IV Statistical tables
1 Numbering of tables
(1) There are three kinds of numbers, i.e., a section number, a main number and a branch number. Both section number and main number
start with 1 in numerical order and a branch number starts with "a" in alphabetical order.
(2) In the following cases, branch numbers are attached to the same main number.
Under the same category :
① Different boxhead classification by year is presented.
② Actual figures and processed figures based on the actual figures are both presented by separate tables.
③ Indexes are based on different base years.
④ Contents and base year of indexes are the same, but classification (by districts, items, annual average, average of fiscal year) is different.
2 Indication of the period covered
The beginning year and the ending year are indicated within ( ) following the title.
(1) Where years are consecutive, the beginning year and the ending year are connected by "~" regardless of partial disconnection of years in-between.
(2) Where periodic surveys are conducted with the interval of some years, the beginning year and the ending year are connected by "…."
3 Indication of unit
In principle, unit is placed in the top margin of the table. If units are different by items, they are shown in the boxhead of the respective items. When the unit of the item is changed during the period, the latest unit is shown in the boxhead of the item.
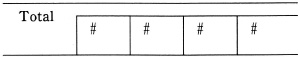
4 Itemization
Where a total is not divided into all component items and has some omissions, "#" is marked in the upper left corner of the respective items. However, when only the unknown item is omitted, "#" is not shown.

5 When English translation is too long to insert in the boxhead or stub
(a), (b), ……, are marked in the respective places and the translation is shown in the last part following footnotes.
6 In principle, years of both the Japanese era and the Christian era are shown in the stub of the table.
7 Reference tables
Following the last table of statistics of each section, reference tables are presented in such cases as below.
(1) Data are published by the government or government-affiliated agencies,
① but the covering period is too short for time-series comparison,
② but accuracy is questionable, however, the data are thought to be informative since such data are not included in the main table,
③ but the subject of survey is particularly limited.
(2) The item is too specialized and not appropriate to insert in the main table, but thought to be necessary.
(3) Data are calculated with reference to the rate of increase over the preceding year or the percent distribution.
(4) Consistent and historical data since the Meiji era are obtainable from the estimates by learned people.
V Footnotes
1 In principle, notes are presented as footnotes. Where no space is available in the lower margin, they are placed in "Note" following statistical tables and (Note) p. XXX is shown at the end of the footnote.
2 Footnote
(1) Footnotes applying to whole data are shown in numerical order with ( ) in a way such as (1), (2), ……, but these numbers do not appear in the corresponding places in the table.
(2) Marks such as 1), 2), ……, and a), b), ……, in the table indicate the corresponding footnotes respectively.
① 1), 2), ……, are attached to the title, margin, boxhead, and stub of the table.
② a), b), ……, are attached to figures in the table.
(3) Footnotes for "Source" and numbers with ( ) are described only in the first page and not in the continuing pages, whereas, footnotes for 1), 2), ……, are described in all continuing pages concerned.
3 In the first part of a footnote, "Source" indicates the name of the authorities concerned and the name of the survey or data. If the data are based on those for internal use of a ministry concerned and not published, it indicates "Data of Ministry of XXX." When the name of a survey (or a source) is changed, only the latest name is shown.
4 Where conversion of unit or computation for linking indexes is made by the Statistics Bureau, notes indicating "Computed by the Statistics Bureau, Management and Coordination Agency," the coefficient of conversion and the method of computation are described .
VI Note and source
"Note and source" presents the original source of the respective data and notes. However, the sources are available only in Japanese.
VII Marks in the table including the indication of discontinuity
1 Marks in the table
-- : Figures cannot exist, or possibly exist but practically nil.
0 : Figures below unit
x : Figures withheld
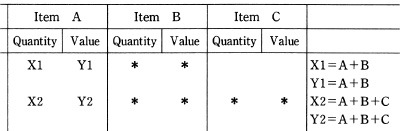
* : Where several items are summed, figures are presented only in the first column and * is marked in other columns.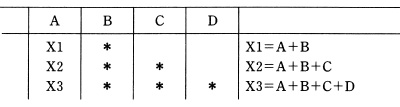
…
: Figures not available (unknown).0 : Figures below unit
x : Figures withheld
* : Where several items are summed, figures are presented only in the first column and * is marked in other columns.
(Example 1)

(Example 2)

2 Indication of discontinuity
Where the discontinuity of figures exists between years, that portion is indicated with …… or ---- to invite attention. The reason is described in the margin or the footnote of the table.
(1) Where a unit or a brand of commodity changes considerably, that portion is indicated with …….
(2) Where figures of different nature, such as permanent domicile population and census population, are arranged in the same table, the discontinuity is indicated with ----.
Besides the above, necessary parts are indicated with ……or ---- with the explanation in a footnote.